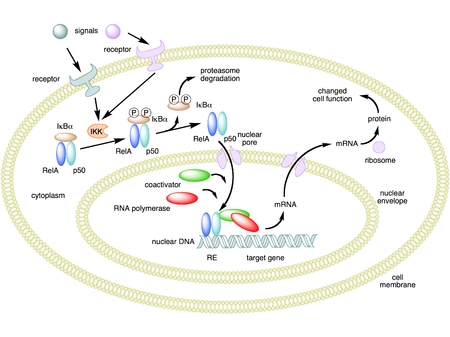
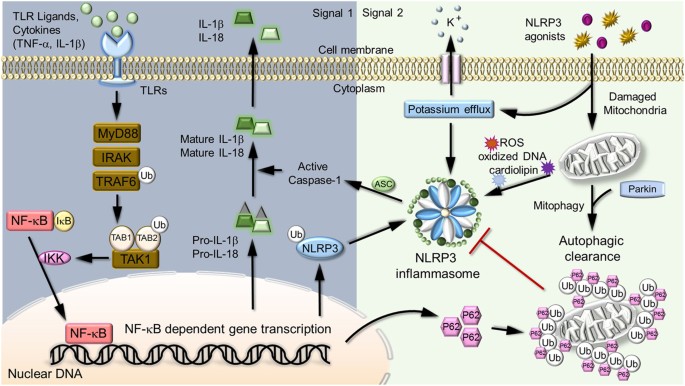
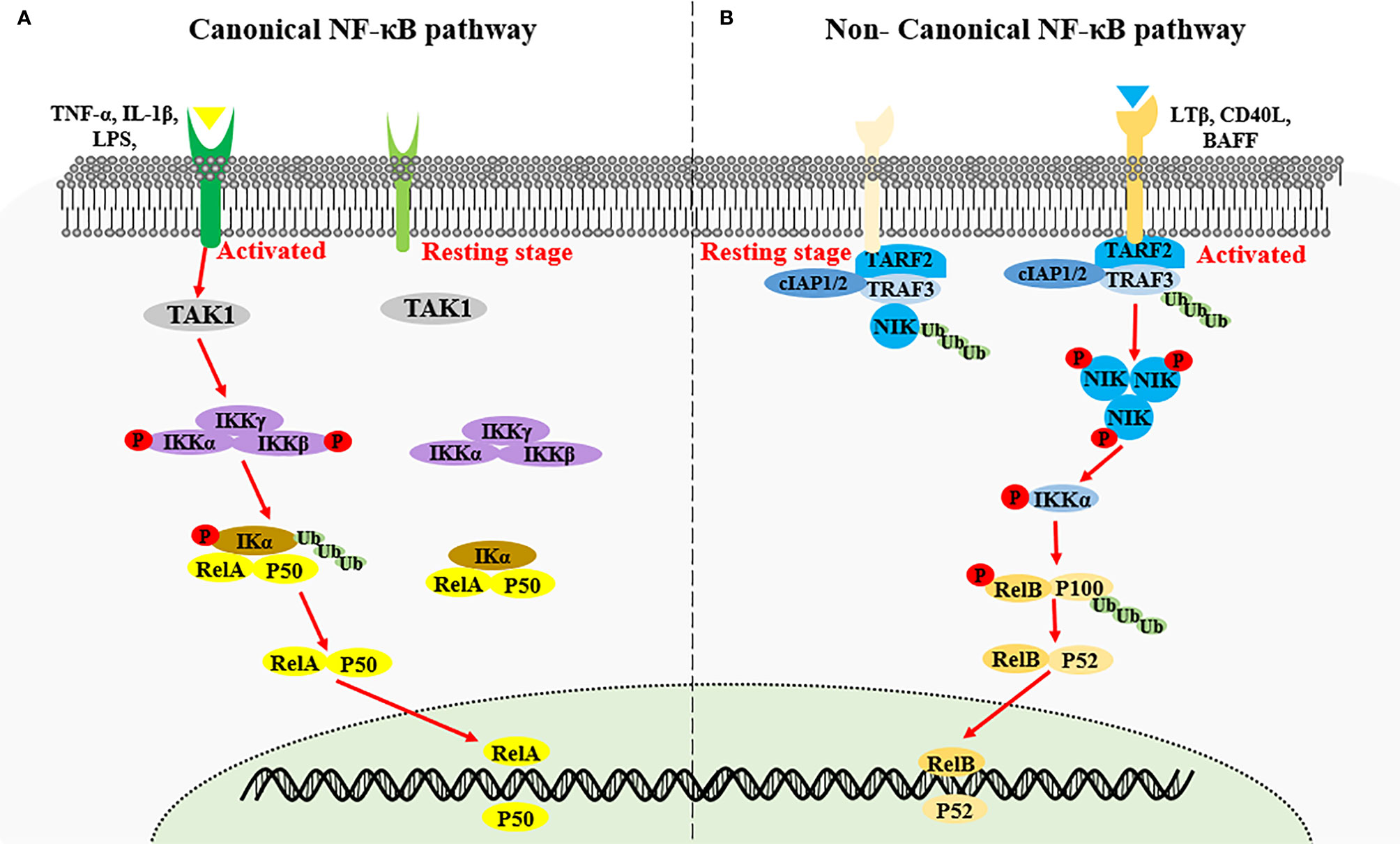
An epithelial Nfkb2 pathway exacerbates intestinal inflammation by supplementing latent RelA dimers to the canonical NF-κB module | PNAS

NF‐κB in inflammatory bowel disease - Atreya - 2008 - Journal of Internal Medicine - Wiley Online Library
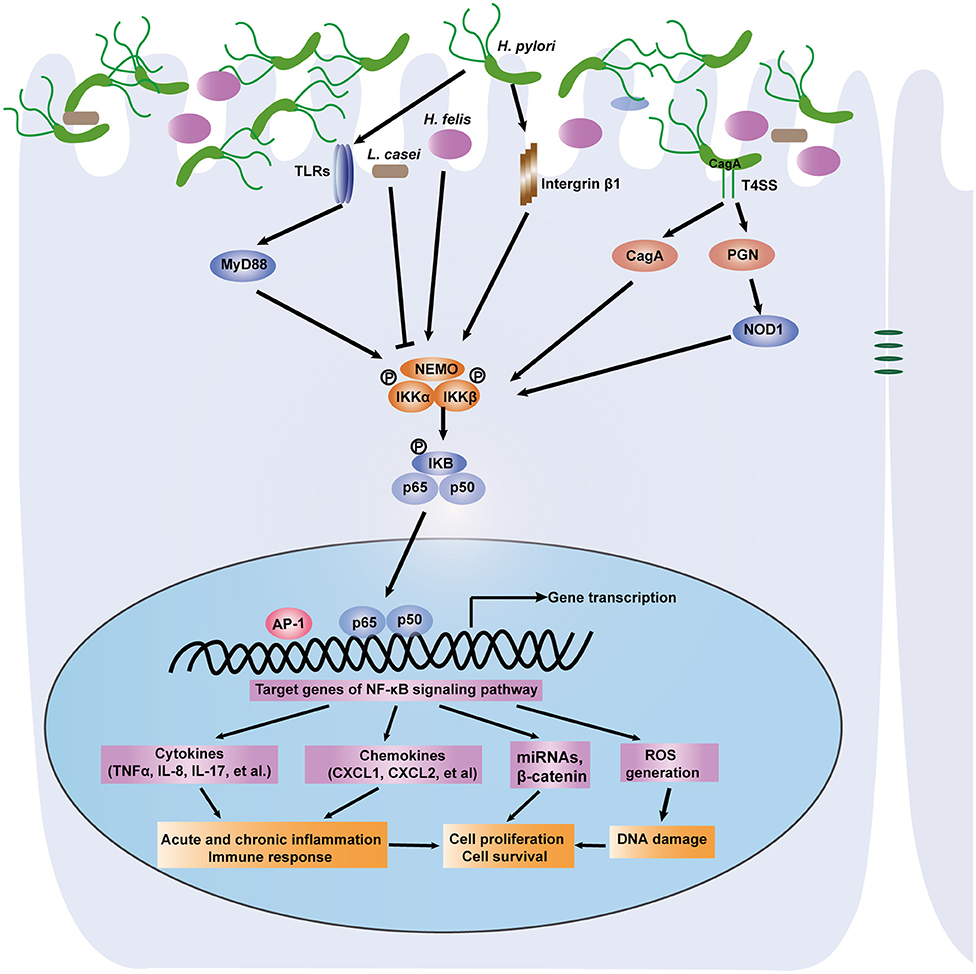
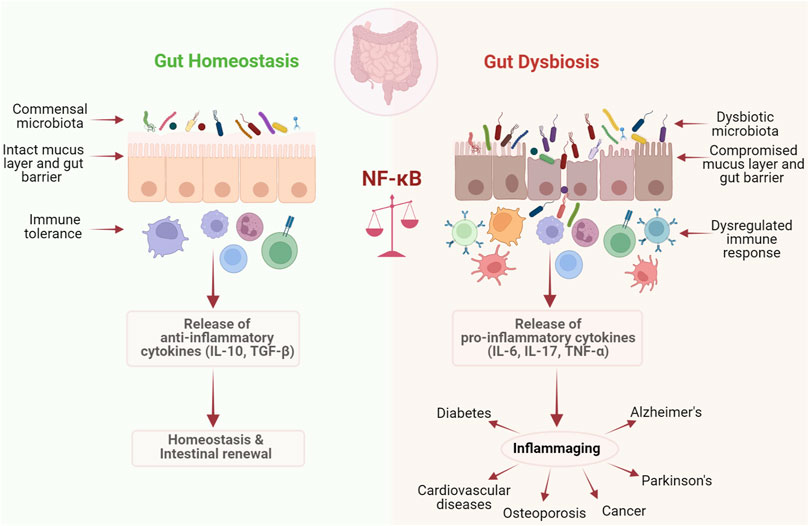
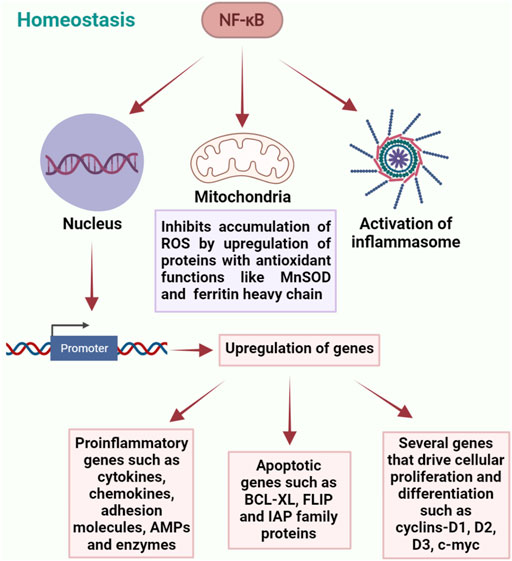
Frontiers | The NF-κB Signaling Pathway, the Microbiota, and Gastrointestinal Tumorigenesis: Recent Advances

Intestinal non-canonical NFκB signaling shapes the local and systemic immune response | Nature Communications
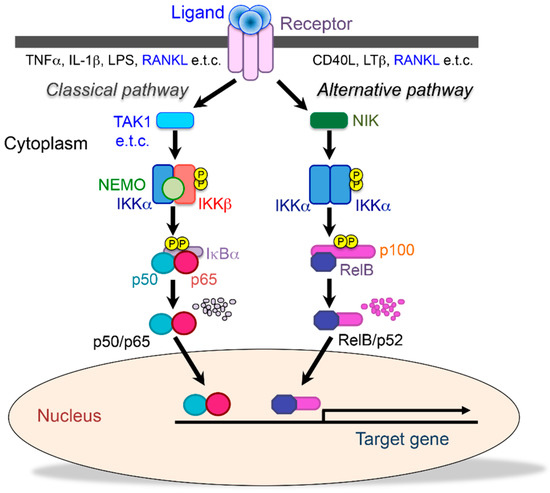
Cells | Free Full-Text | The Role of NF-κB in Physiological Bone Development and Inflammatory Bone Diseases: Is NF-κB Inhibition “Killing Two Birds with One Stone”?

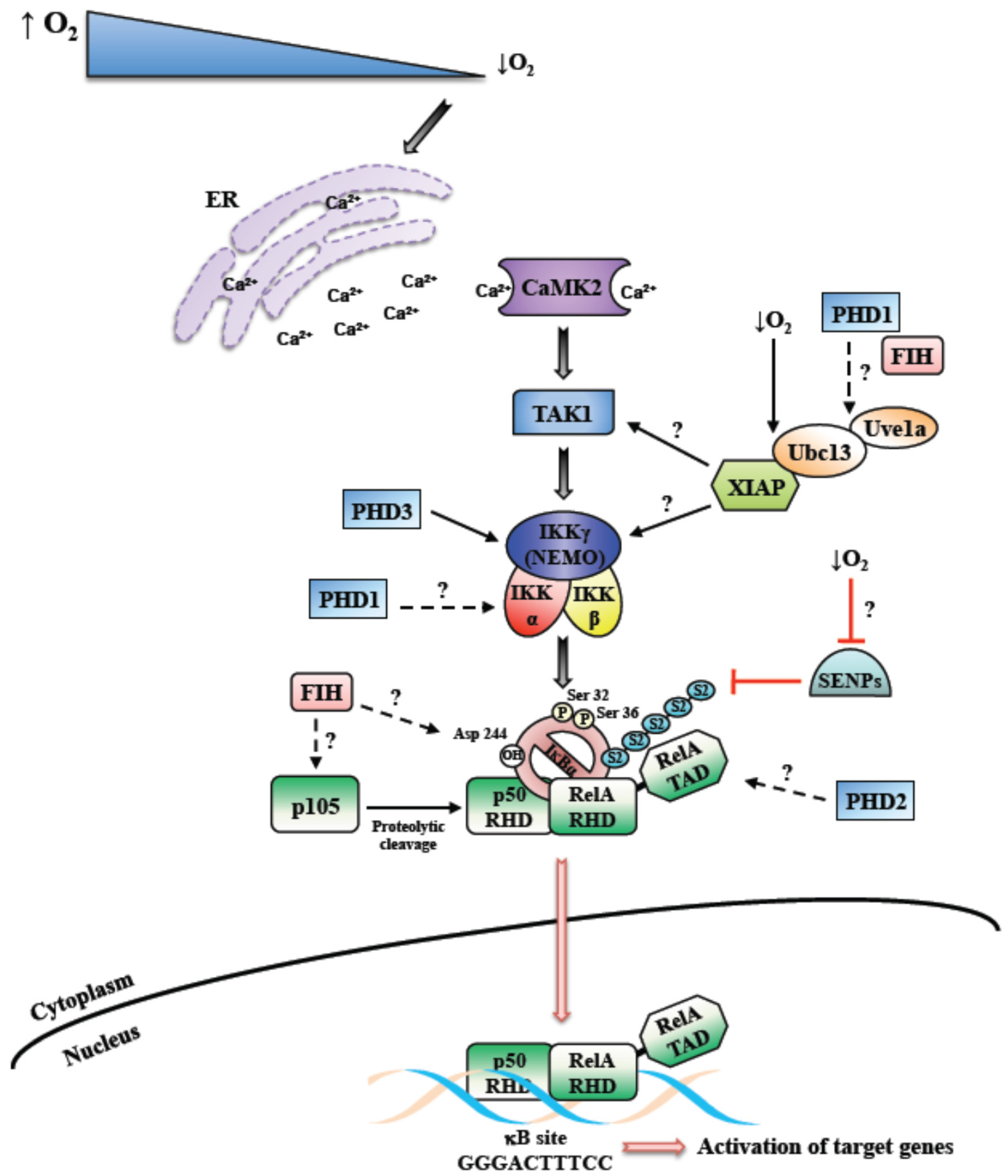
NF-κB activation as a pathological mechanism of septic shock and inflammation | American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology
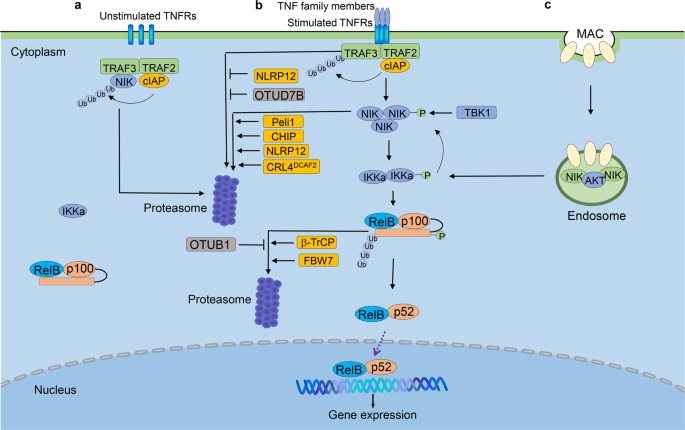
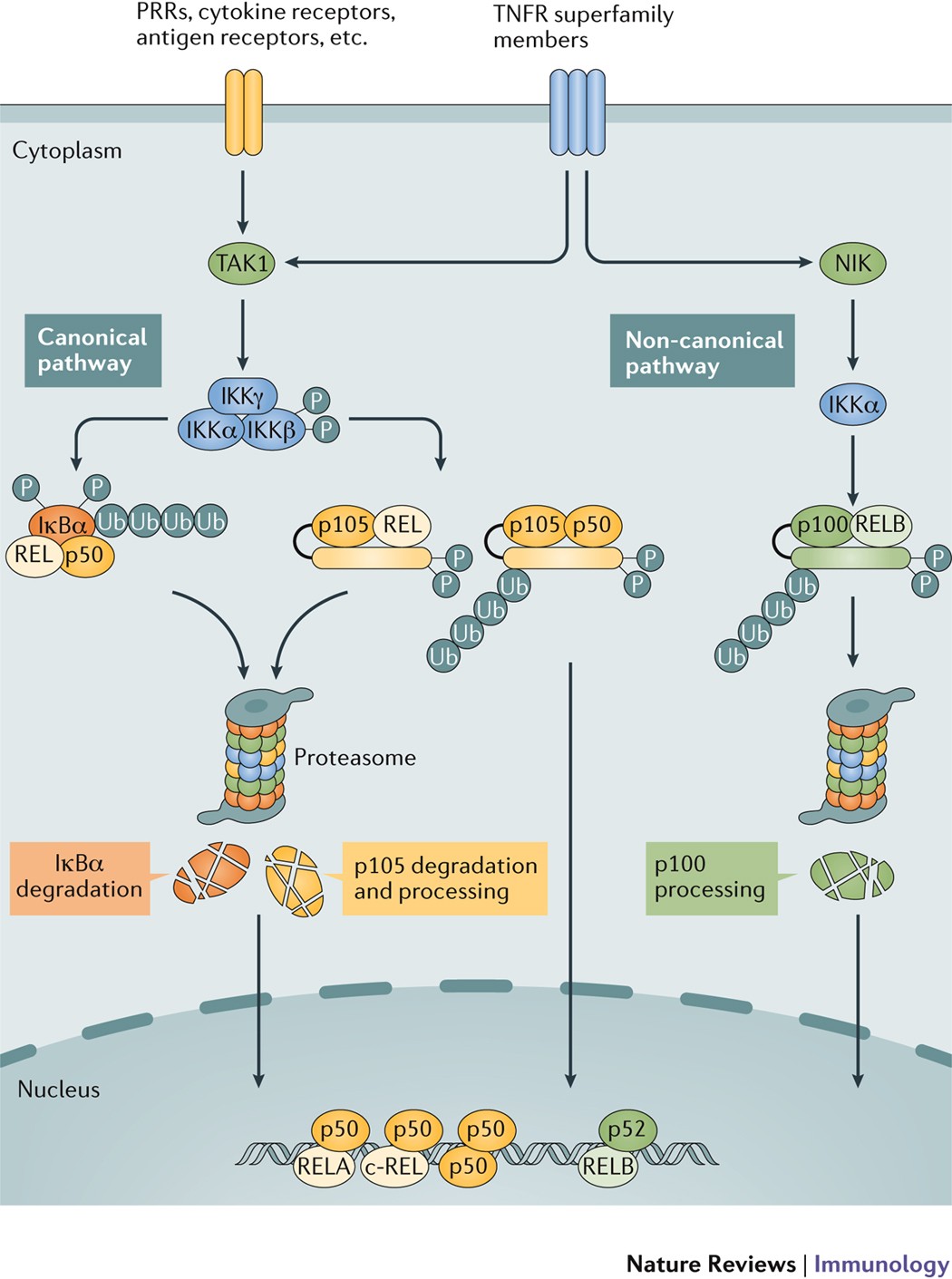
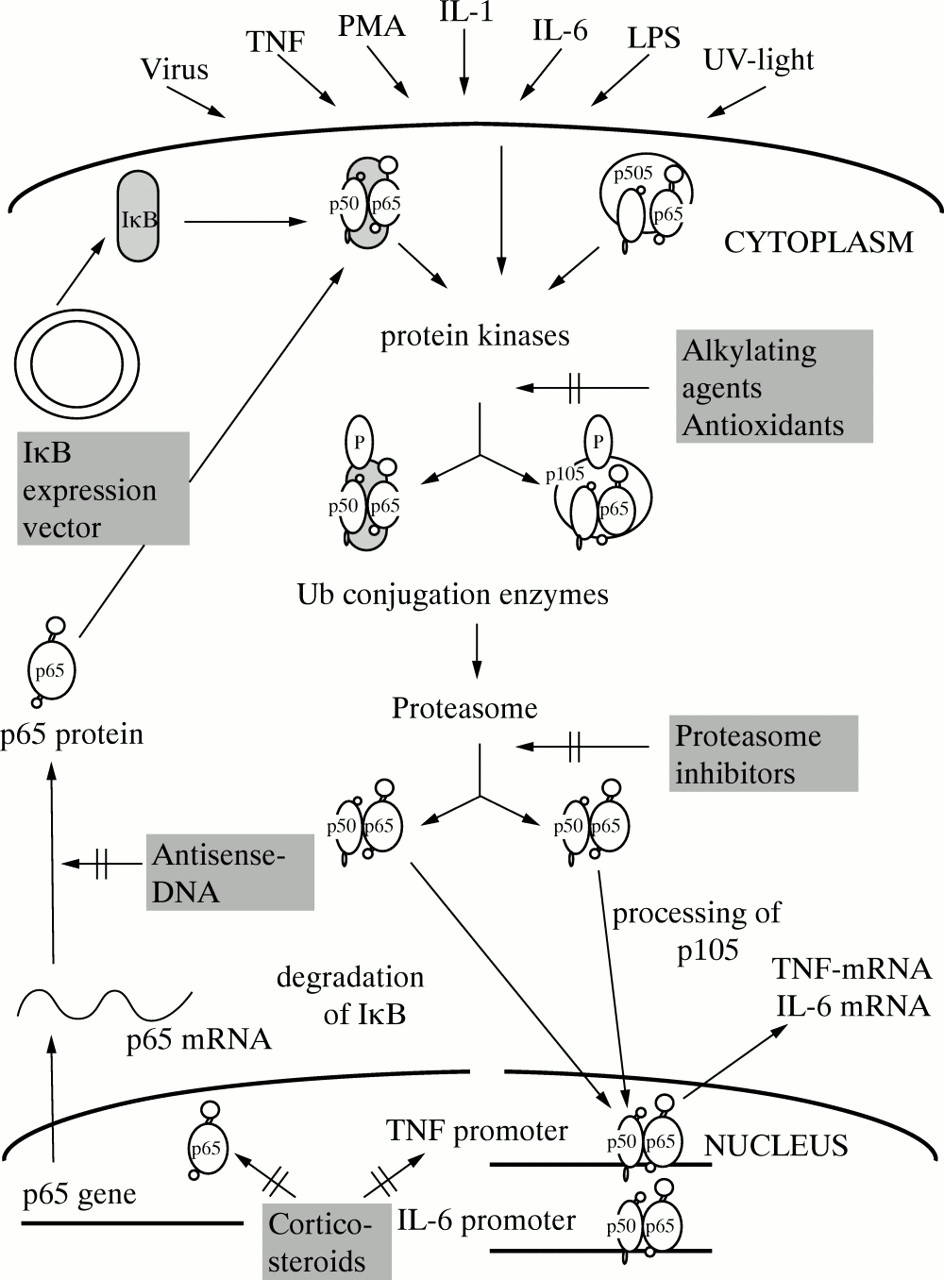
Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: mechanism and clinical study | Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy
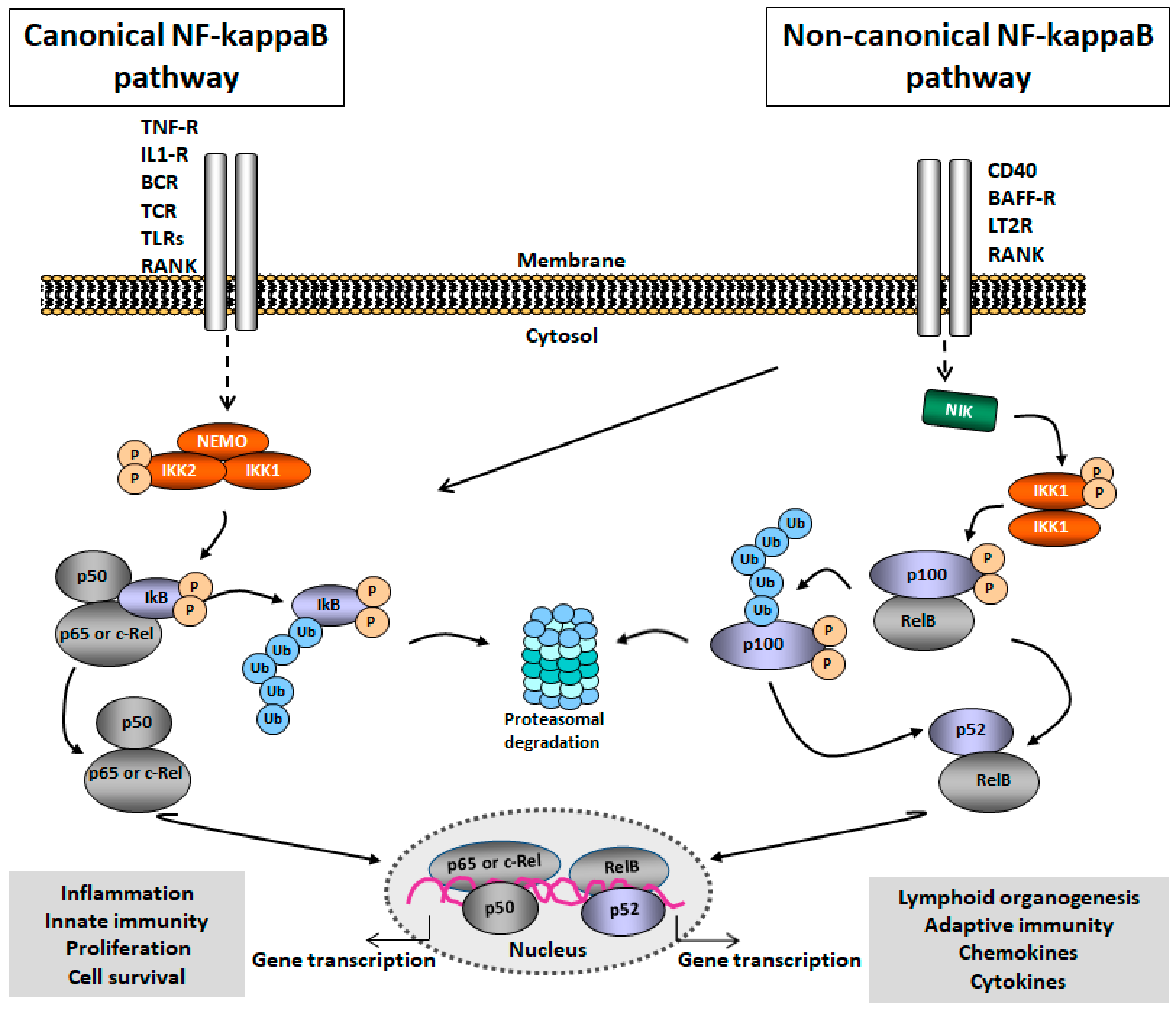
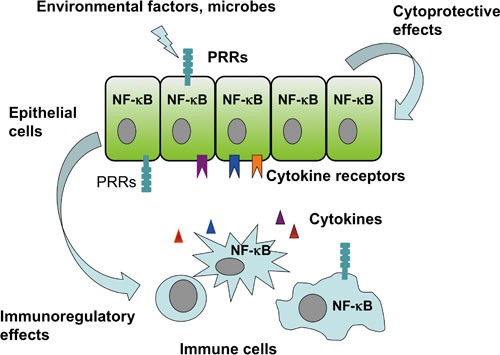
Cells | Free Full-Text | Cell-Type Targeted NF-kappaB Inhibition for the Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases
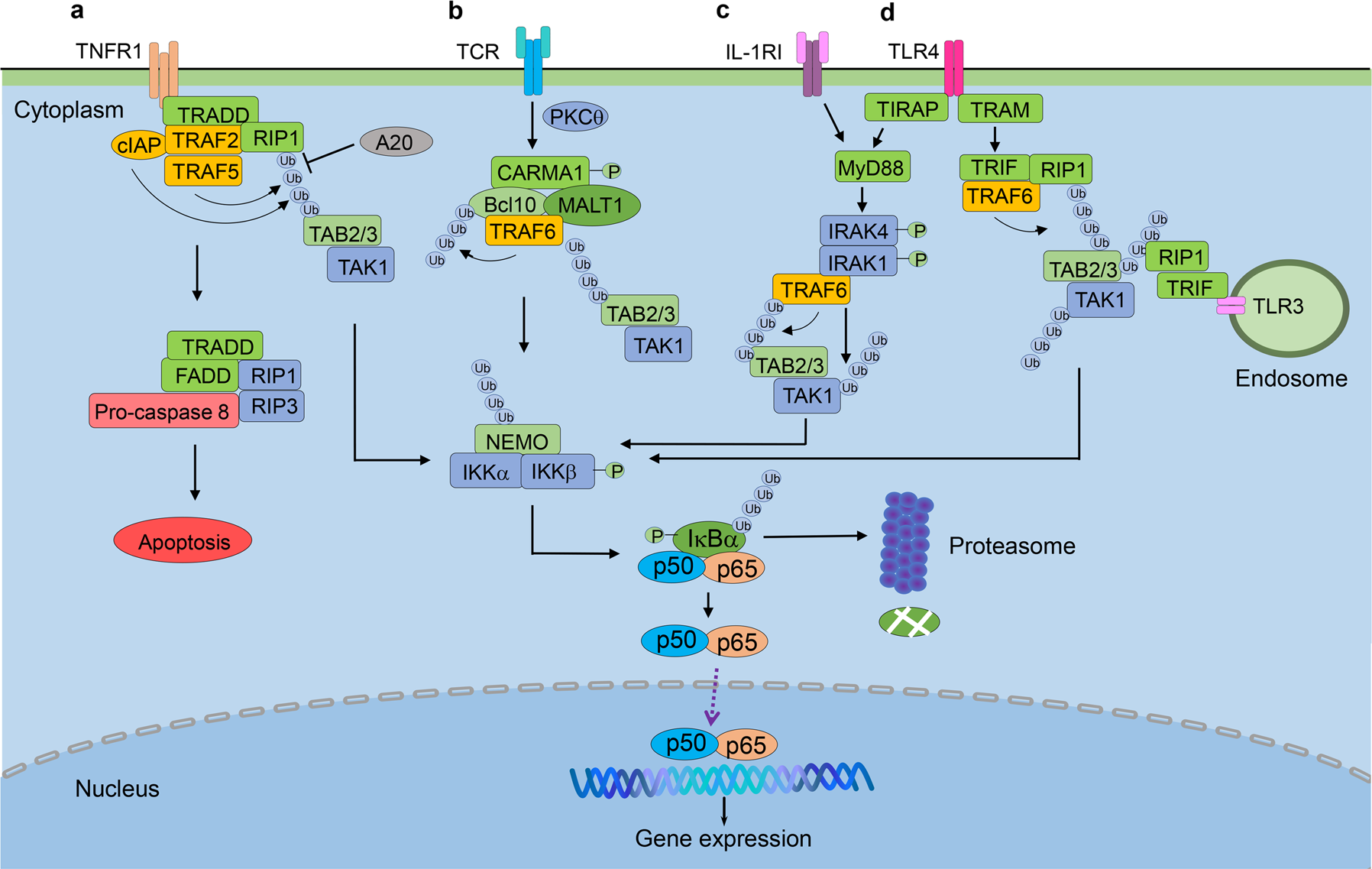
Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: mechanism and clinical study | Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy
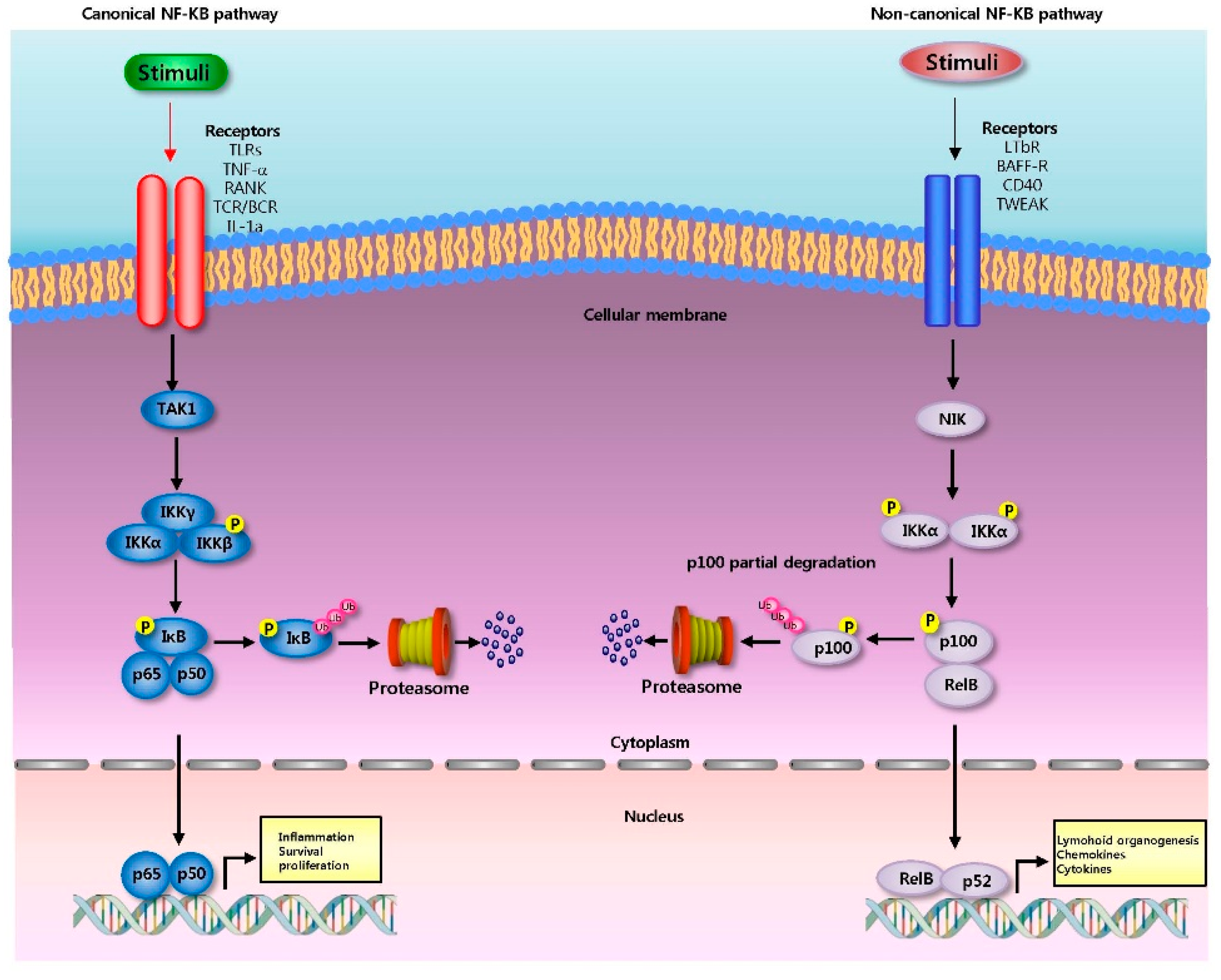
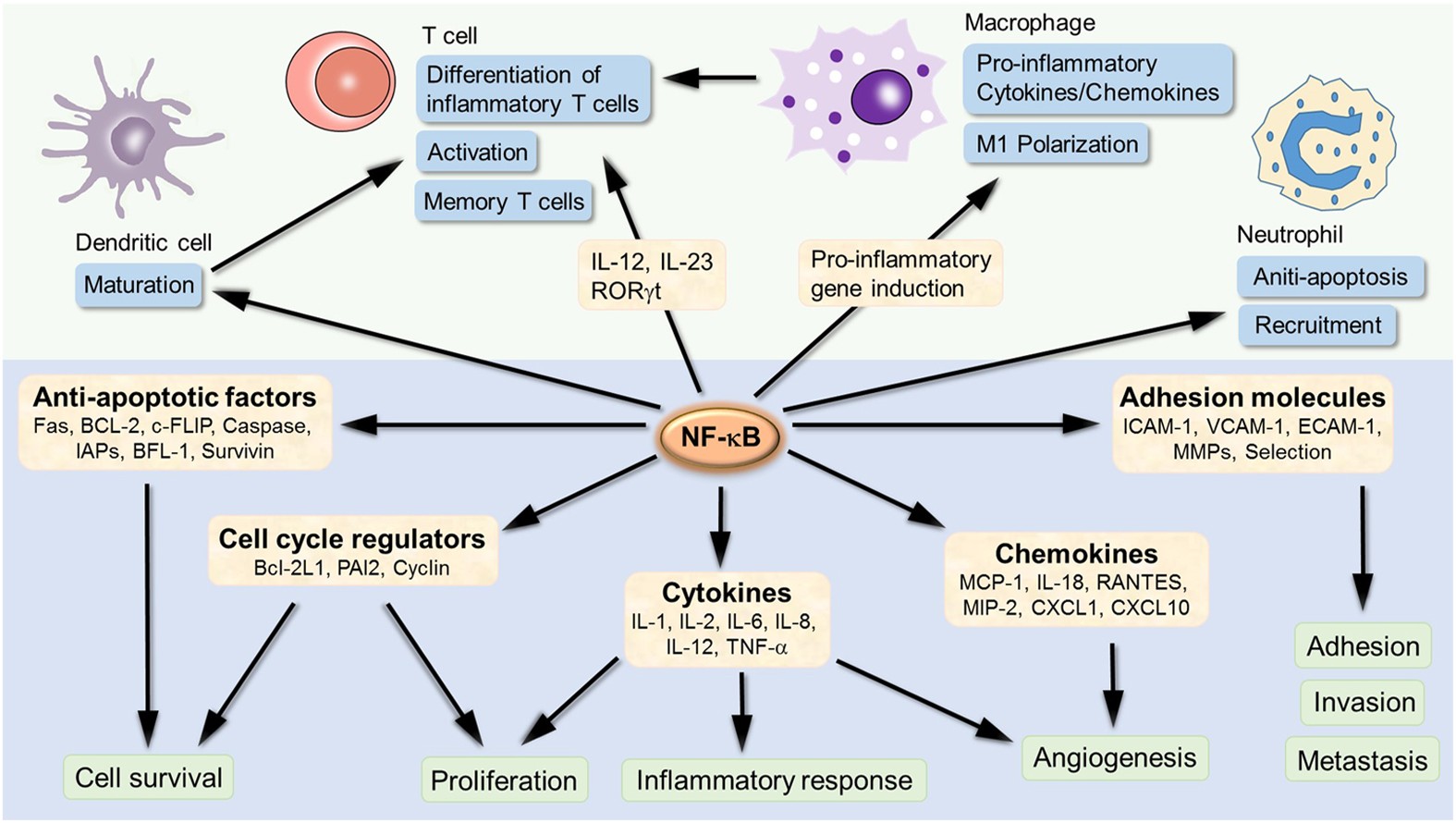
Cells | Free Full-Text | Roles of NF-κB in Cancer and Inflammatory Diseases and Their Therapeutic Approaches

An epithelial Nfkb2 pathway exacerbates intestinal inflammation by supplementing latent RelA dimers to the canonical NF-κB module | PNAS

NF-κB and Extrinsic Cell Death Pathways – Entwined Do-or-Die Decisions for T cells: Trends in Immunology
NF-kappa-B activation unveils the presence of inflammatory hotspots in human gut xenografts | PLOS ONE
NF-kappa-B activation unveils the presence of inflammatory hotspots in human gut xenografts | PLOS ONE
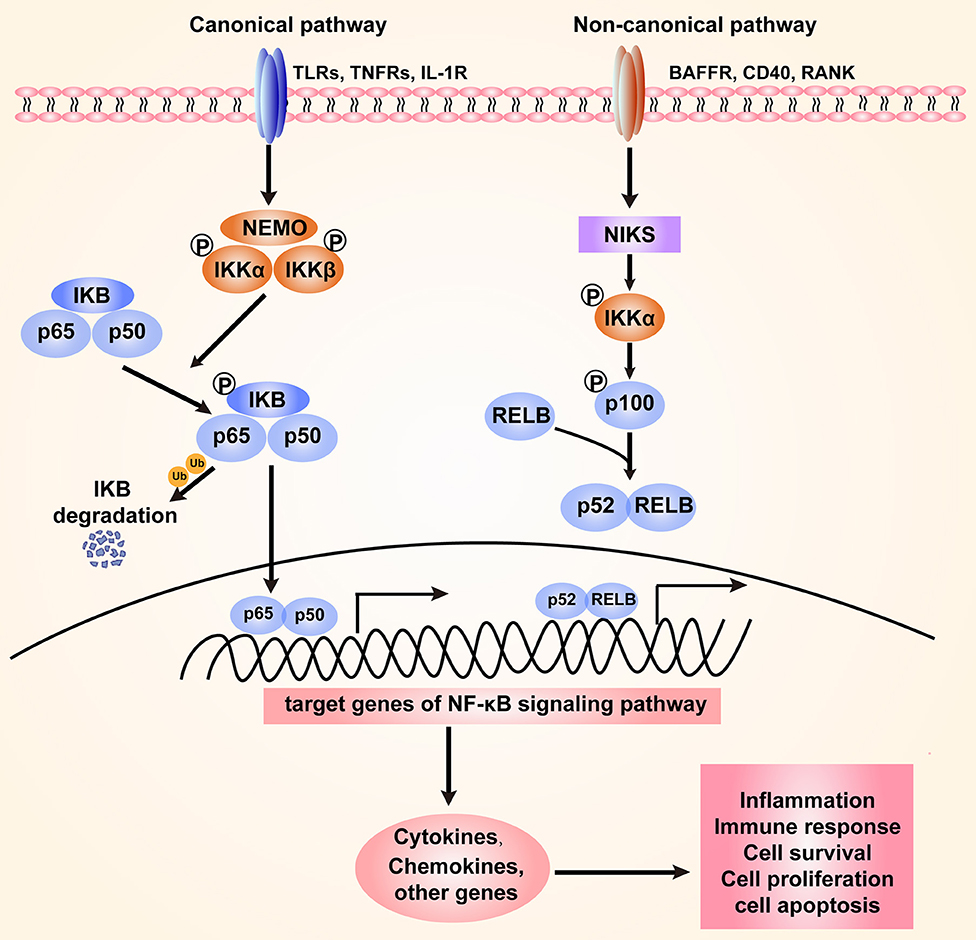
Frontiers | The NF-κB Signaling Pathway, the Microbiota, and Gastrointestinal Tumorigenesis: Recent Advances